Definition Right Brain vs. Left Brain
This theory of the structure and functions of the mind suggests that the two different sides of the brain control two different “modes” of thinking. It also suggests that each of us prefers one mode over the other.
Discussion
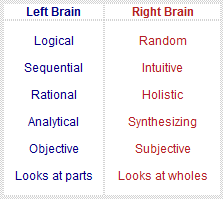
Experimentation has shown that the two different sides, or hemispheres, of the brain are responsible for different manners of thinking. The following table illustrates the differences between left-brain and right-brain thinking:
Most individuals have a distinct preference for one of these styles of thinking. Some, however, are more whole-brained and equally adept at both modes.
In general, schools tend to favor left-brain modes of thinking, while downplaying the right-brain ones. Left-brain scholastic subjects focus on logical thinking, analysis, and accuracy. Right-brained subjects, on the other hand, focus on aesthetics, feeling, and creativity.
How Right-Brain vs. Left-Brain Thinking Impacts Learning
Curriculum–In order to be more “whole-brained” in their orientation, schools need to give equal weight to the arts, creativity, and the skills of imagination and synthesis.
Instruction–To foster a more whole-brained scholastic experience, teachers should use instruction techniques that connect with both sides of the brain. They can increase their classroom’s right-brain learning activities by incorporating more patterning, metaphors, analogies, role playing, visuals, and movement into their reading, calculation, and analytical activities.
Assessment–For a more accurate whole-brained evaluation of student learning, educators must develop new forms of assessment that honor right-brained talents and skills.
We also offer teaching techniques for right brain and left brain students and information about right brain vs. left brain functions in learning.
Reading
Bernice McCarthy, The 4-MAT System: Teaching to Learning Styles with Right/Left Mode Techniques.
Note: This article has been edited by Funderstanding