How States and Federal Government Argue
(And Why It’s Actually Pretty Cool!)
Kids should see that America works like a team: the federal government sets nationwide basics, states adjust for local needs, and the Supreme Court is the referee when they clash.
4:14
Overview
Kids live with lots of rules every day—from what you learn in school to when you cross the street. Knowing why different places can have different rules helps you understand why your town, your state, and Washington sometimes disagree. These conversations show how teamwork and fair play keep everyone safe, happy, and heard. Talking about it also makes it easier to spot rule changes on road trips, at school, or even on family game night.

Understand in 30 Seconds
Get up to speed quickly
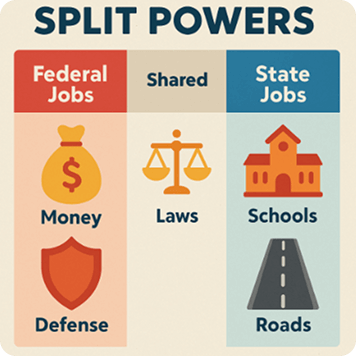
- Two Job Descriptions: Federal leaders handle country-wide issues—money, defense, big safety laws. States handle things closer to home—schools, roads, local safety.
- Built-in Tension: The Constitution divides power on purpose so no one level gets too bossy.
- Referee on Call: When a rule fight breaks out, the Supreme Court decides whose playbook wins.
- Why It Matters to You: These decisions shape what you learn in school, how clean your air is, and even which road signs you see.
Real Life Scenario
Situations you can relate to
Have you ever argued with a sibling about bedtime? Mom and Dad set the main bedtime—like Washington sets big rules—but you and your sibling might negotiate extra story time—like states tweaking smaller rules.
What if you could stay up 15 minutes later to finish a book? And your sibling wants 30 more minutes to play a game? How do you all agree?
If you can't, you might ask Grandma to settle the tie—just like the Supreme Court steps in when states and Washington don't agree. In the end, everyone learns to compromise and keeps the adventure going smoothly.

Role Play
Spark a conversation with “what if” scenarios
What if every state could print its own money—what problems might pop up on a family vacation?
- Role play: Pretend you're driving through five different states on a road trip, and each one has its own kind of money. How would you buy snacks or gas? What might go wrong or be tricky?
What if the Supreme Court didn't exist—how would arguments between states and the federal government ever end?
- Role play: Imagine you're in charge of the country and two states are having a big argument. There's no Supreme Court. What would you do to help them settle it fairly? Who would you trust to decide?
What if your town wanted a speed limit very different from the state's—who should decide?
- Role play: Say you're the mayor of your town and you want the speed limit to be much lower than the state law says. How would you explain your reasons? Who might push back—and how could you convince them your rule is safer?
FAQs
Frequently asked questions people want to know
Who decides what power belongs to states?
The Constitution lists federal powers; anything not listed usually belongs to states.
Can a state ignore a federal law it dislikes?
Not for long—if conflict continues, federal courts can require the state to follow national law.
Why does the Supreme Court get the last word?
The Court's main job is to interpret the Constitution, so its rulings settle disagreements about what the rules really mean.
Examples in the Wild
See how this works day to day
- In 2021, California sued the federal government to keep its tougher car-pollution standards, saying it needed cleaner air for its people (Reuters)
- Colorado has allowed recreational marijuana since 2012, even though federal law still bans it—creating daily questions for banks, businesses, and police (americanbar.org)
- In 2022, the Supreme Court blocked the federal vaccine mandate for large companies (NFIB v. OSHA), sending decisions back to states and employers (nfib.com)
- In 2015, the Supreme Court's Obergefell v. Hodges ruling said every state must allow same-sex marriage, making one national rule for weddings (oyez.org)
In Summary
What you should know before you start
- Federal rules cover the whole country; state rules fine tune life closer to home.
- Power sharing is intentional so no single level gets too strong.
- Arguments are normal and often improve the final decision.
- The Supreme Court keeps the game fair when rules collide.
Pro-tip for Parents
You got this!
Kids may feel frustrated when rules differ from place to place ("Why is the speed limit higher in the next state?"). Acknowledge the confusion, then turn it into a mini game: spot differences on your next drive and guess why that state made that choice—showing that diverse solutions help a big country meet many needs.
Keep an Eye Out For
Find these examples in everyday life
- News about states adding (or losing) special pollution waivers.
- Court cases where states challenge federal education rules.
- Headlines on changing drug policy laws across different states.
Explore Beyond
Look up these related research topics
- How a Bill Becomes a Law
- Checks and Balances among the three branches
- The Electoral College and state influence